Measurements code |
Measured value |
Preferred method of measurement |
C1 |
Arterial systemic pressure |
Direct manometry. Invasive pressure sensor in the aorta or other major arteries of systemic circulation |
C2 |
Arterial pulmonary pressure |
Direct manometry. Invasive pressure sensor in the pulmonary artery |
C3 |
Venous systemic pressure |
Direct manometry. Invasive pressure sensor in a large vein systemic circulation |
C4 |
Venous pulmonary pressure |
Direct manometry. Invasive pressure sensor in the pulmonary vein |
C5 |
Left ventricular pressure |
Direct manometry. Invasive pressure sensor in the left ventricle |
C6 |
Right ventricular pressure |
Direct manometry. Invasive pressure sensor in the right ventricle |
C7 |
Blood flow through the aortic valve |
Measurement of blood flow. Sensor of blood flow in the ascending arc of the aorta |
C8 |
Blood flow through the mitral valve |
Measurement of blood flow. Sensor of blood flow in the pulmonary vein |
C9 |
Blood flow through the pulmonary artery valve |
Measurement of blood flow. Sensor of blood flow in the pulmonary artery |
C10 |
Blood flow through the tricuspid valve |
Measurement of blood flow. Sensor of blood flow to the systemic vein |
C11 |
Left ventricular volume |
| Indirectly, as |
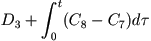 |
(78) |
|
C12 |
Right ventricular volume |
| Indirectly, as |
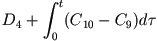 |
(79) |
|