Measurement of blood oxygenation
Oxymetry is measuring the relative content of oxygenated hemoglobin in the blood, which is a numerical measure of the value of the blood saturation SpO2. Saturation is calculated as the ratio of oxygenated hemoglobin HeO2 to the total quantity of hemoglobin He :
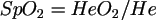 |
(80) |
The work of the device based on ability and non-oxygen hemoglobin absorb light of different wavelengths. Oxygenated hemoglobin absorbs more infrared light, non-oxygenated hemoglobin absorbs more red light. In oksimetre has two LEDs, emitting red and infrared light. At the receiving part is a photo sensor, which determines the intensity of light falling on it flow. By measuring the difference between the amount of light absorbed during the cardiac cycle, oksimetr could fix the curve of arterial pulsation. In clinical practice, using invasive and non-invasive methods of oxymetry.
Invasive measurement methods require the introduction of fiber-optic catheter with a sensor in the monitoring of the blood channel. An important advantage of invasive oxymetry is the possibility of measuring virtually any part of the vascular channel. The main disadvantage is the need to introduce in the bloodstream of a measuring device. Invasive oxymetry actually surgery and may be performed only in a hospital environment.
Non-invasive measurement methods have a common name of pulse-oxymetry. The disadvantage of non-invasive pulse-oxymetry is a significant influence of external factors on the accuracy of measurements. These factors may be a bright external light and movement. The work unit may also violate the improper location of the sensor. For transmission oxymeter (working in the lumen), it is necessary that both parts of the sensor were symmetrical, otherwise the path between the photodetectors and LEDs will be unequal, and one of the wavelengths will be «loaded». This deficiency deprived refractive (working on reflection) pulse-oxymeter.
Identification > Measurements > Methods of measurement > Measurement of blood oxygenation
References on the topic:
© Samara-Dialog Ltd. 2004-2009 |