|
Identification > Measurements > Measuring paradigm
|
Measuring paradigm
At statement of a problem of identification we are limited to measurements of periodic movements [25].
As an interval of time of measurements one warm cycle is accepted. It is made for following practical reasons:
There are various methods of measurement of physiological sizes. The most essential features of these methods at statement of a problem of identification in [25] have been named by a measuring paradigm. Three basic measuring paradigms are allocated.
Paradigm C. Paradigm of continuous measurements. The vector of measurements is defined as analytical function from a vector of a condition and a vector of parametres during any moment of time on an interval of time of supervision according to the formula:
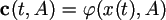 |
(75) |
Paradigm D. Paradigm of measurements during the chosen moments of a cardiac cycle. Vectors of measurements are defined as analytical functions from a vector of a condition and a vector of parametres during the chosen moments of time on an interval of time of supervision according to the formula:
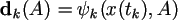 |
(76) |
Paradigm I. Paradigm of integrated measurements. The haemodynamic sizes integrated on all interval of time of supervision are measured. The vector of measurements is defined as functional from a trajectory on an interval of time of supervision and a vector of parametres according to the formula:
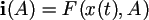 |
(77) |
Identification > Measurements > Measuring paradigm
References on the topic:
© Samara-Dialog Ltd. 2004-2009 |